Design Youtube.
Same like Amazon Prime, Netflix.
Estimation.
Total monthly active user - 2billion.
Number of videos watched per day - 5billion.
50 million creator on Youtube. 80% Us adult see youtube. Majority in mobile internet traffic.
Youtube is available in 85 different language.
There are lot of things to be done in youtube like comment, like, save a playlist, share, subscribe to a channel. Not possible to design all. Get the scope of the design.
Main feature to design - Ability to upload a video and watch a video.
Client to support - Mobile, Web browser and smartTv.
DAU - 5 million.
Average daily time spend - 30 mins.
Supported video resolution - most of the video resolution formats.
Encryption - Required.
File size requirement - Small and medium size videos. Max allowed size - 1GB.
Use exiting cloud infrastructure like Amazon, Google, Microsoft - Yes. Functional Requirement.
Ability to upload video fast.
Smooth video streaming.
Ability to change video quality.
Low infrastructure cost.
High availability, scalability, reliability requirements.
Client supported - mobile apps, browser, smartTv.
Back Of the Envelope Estimation.
User watch 5 videos per day. DAU 5 million. 10 % of user upload 1 video per day.
Average video size 300 MB. Total daily storage space needed 5 million10% 300MB = 150TB.
CDN cost - When cloud CDN serves a video - it is charged for the data transferred out of the CDN. Example Amazon CDN CloudFront - Assume 100% traffic is served from the US. The average cost per GB is $0.02.
The cost of video streaming = 5 million * 5 videos * 0.3GN * $0.02 = $ 150,000 per day. Cost of serving video from the CDN costs a lot of money.
High level Design.
Use an existing cloud services - CDN and blob are good example.
Leaning - Use the right technology more imp than explaining the technology internal work. Example - blob storage for storing video is enough discussing the internal of blob storage is overkill. Netflix uses Amazon cloud service and Facebook uses Akamai.
At a high level system comprises 3 components - Client - Watching videos in mobile, laptop. CDN - Video is stored in CDN and when click on play the video is streamed from CDN. API Servers - Everything else except video streaming goes to the API servers - feed recommendation, generating video upload URL, updating metadata database and cache, user signup.
Interviewer showing interest in two part - video upload and video streaming.
Upload a video.
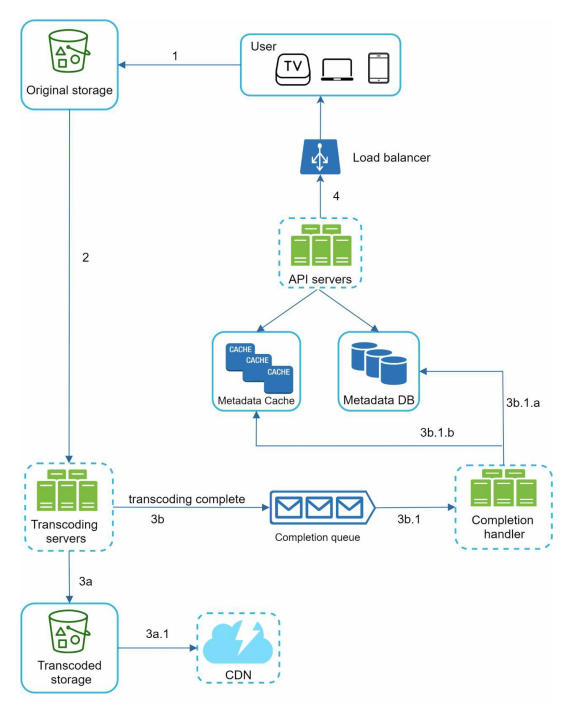
API server - All user requests go to the API servers except video streaming.
Metadata DB - Video metadata are stored in Metadata db. It is sharded and replicated to meet performance and high availability.
Metadata cache - The video metadata and user objects are cached.
Original storage - Blob storage - Binary Large Object.
Transcoding servers - Video transcoding also called video encoding. It is the process of converting a video format to other format MPEG, HLS which provide the best video streams different device and bandwidth capabilities.
Transcoded storage - BLOB storage that store transcoded video files.
CDN - Video are cached in CDN and when the play button is clicked the video is streamed from CDN.
Completion queue - It is a message queue that stores information about video transcoding completion events.
Completion handler - It consists of list of workers that pull event data from the completion queue and update metadata cache and database.
Video uploading flow is broken down in two process - upload the actual video and upload the metadata. Metadata consists of video URL, size, resolution, format, user info.
1 - Video are uploaded to the original storage.
2 - Transcoding server fetch videos from the original storage and start transcoding.
3 - Once transcoding is complete, the steps executed in parallel - 3a. Transcoded videos are sent to transcoded storage. - 3b. Transcoding completion events are queued in the completion queue.
3a.1 - Transcoded videos are distributed to CDN.
3b.1 - Completion handler contains a bunch of workers that pulls events data from the queue.
3b.1.a and 3b.1.b - Completion handler update the metadata database and cache when video transcoding is complete.
4 - API servers inform the client that the video is successfully uploaded and is ready for streaming.
Upload the metadata.
While a file uploaded to the original storage the client parallel send a request to update the video metadata. API server update the metadata cache and database.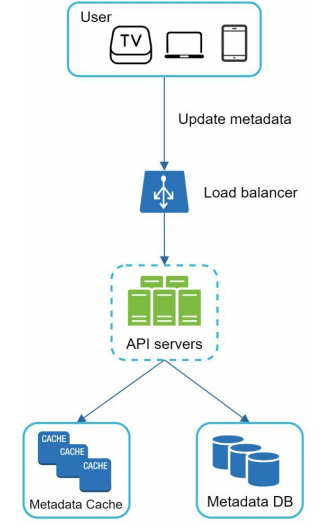
Video Streaming Flow.
YouTube video don’t wait until the video is downloaded. Downloading means the video is copied in the device while streaming means device continuously receives video streams from remote source videos.
When watching streaming video - client load bit of data at a time to watch immediately.
Streaming protocol - Protocol to control data transfer for video streaming. Popular streaming protocol are - MPEG-DASH (”Moving Picture Experts Group”) and DASH (”Dynamic Adaptive Streaming over Http”)
Apple HLS (”Http Live Streaming”).
Microsoft Smooth Streaming.
Adobe Http Dynamic Streaming HDS.
Streaming protocol support different video encoding and playback players. When designing the video streaming service get the right streaming protocol.
Videos are streamed from CDN directly. The edge server closest to you will deliver the video. There is little latency.
Design Deep Dive.
The system is broken down in two part - video uploading and video streaming.
Video Transcoding.
When record a video the device (phone or camera) give the video file in certain format. To play the video smoothly on other device the video must be encoded into compatible bitrates and formats. Bitrates are the rates at which bits are processed over time. Higher bitrate - higher video quality. High bitrate stream need more processing power and fast internet speed.
Video transcoding is important for the following reason -
Raw video consumes large amount of storage space. An hour-long high definition video recorded at 60 frames per second take up to few hundred GB of space.
Many device and browser support certain type of video formats. Theus it is important to encode a video to different formats for compatibility reasons.
To ensure users watch high-quality video with maintaining smooth playback - it is good to deliver high resolution video to ser with high network bandwidth and lower resolution video to the low network bandwidth.
Network conditions can change. To ensure a video is played smoothly switching video quality automatically and manually based on network condition is essential for smooth user experience.
Many types of encoding format are available - they contain - Container and Codecs.
Container - It is like a basket that contains a video file, audio, metadata. Container format can be identified by the extension .avi, .mov, .mp4
Codecs - These are compression and decompression algorithm - reduce the video size while preserving the video quality. The most used video codecs are H.264, VP9, HEVC.
Directed Acyclic Graph DAG Model.
Transcoding a video is expensive and time-consuming. Different content creator have different video processing requirement. Some make watermark on the top of the video, some provide thumbnail, some upload high definition video.
To support different video processing pipeline and maintain high parallelism - add some level of abstraction and let programmer decide what to add. Facebooks streaming video engine uses DAG model - which defines task in stages so they can be executed sequentially or parallelly. In out design we have DAG model to achieve flexibility and parallelism.
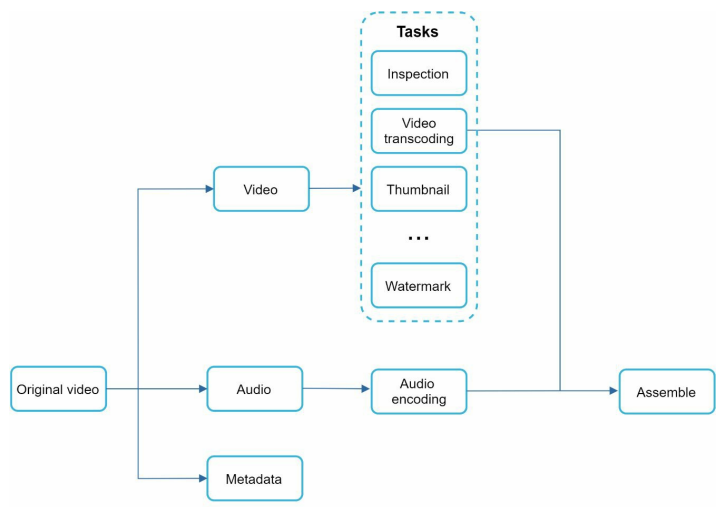
The video is split into video, audio and metadata. Some task that can be applied on video file - Inspection, Video Encoding, Thumbnail, Watermark.
Inspection - Make sure videos are good quality and not malformed.
Video Encoding - Videos are encoded to support different resolutions(144p, 240p, 480p), codec, bitrates.
Thumbnail - Uploaded by user or generated automatically by the system.
Watermark - An image overlay on top of your video contains identifying information about the video.
Video transcoding Architecture.
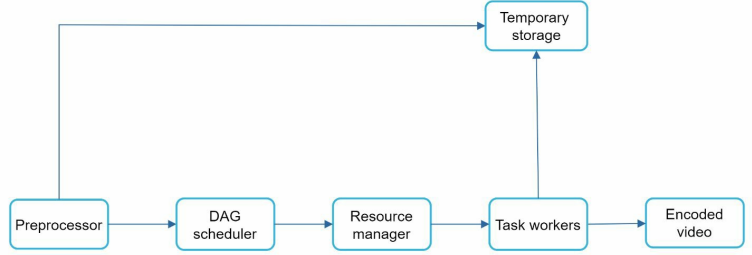
Preprocessor.
Mainly 4 part.
Video Splitting - Video stream is split or further split into smaller Group Of Picture GOP alignment. GOP is a group or chunk of frames arranged in a specific order. Each chunk is an independently playable unit, usually a few seconds in length.
Old mobile does not support video splitting. Preprocessor split video by GOp alignment for old clients.
DAG generation - The processor generated DAG based on configuration files. Example - 2 nodes and 1 edge Download → Transcode.
task {
name 'download-input'
type 'Download'
input {
url config.url
}
output { it ->
context.inputVideo = it.file
}
next 'transcode'
}
task {
name 'transcode'
type 'transcode'
input {
input context.inputVideo
config config.transConfig
}
output { it ->
context.file = it.outputVideo
}
}
Cache data - The preprocessor is a cache for segmented videos. For better reliability, the preprocessor stores GOP and metadata in temporary storage. Video encoding fails the system could use persisted data for retry operations.
DAG scheduler.
It split the DAG graph into stages of tasks and puts them in the task queue in the resource manager.
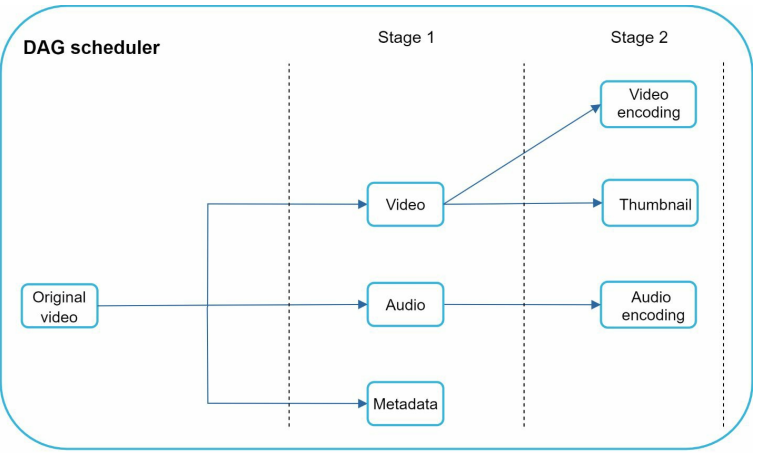
The original video is split into 3 stages - Stage 1 - Video, audio, metadata. the video file is again split into two tasks in stage 2 - video encoding and thumbnail.
The audio file requires audio encoding as part of the Stage 2 tasks.
Resource Manager.
The resource manager is responsible for managing the efficiency of resource allocation. It contains 3 queue and a task scheduler.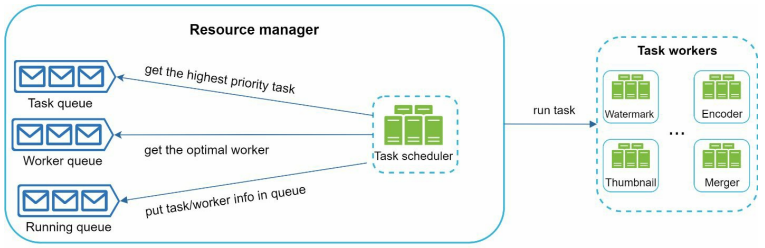
Task Queue - Priority queue that contains tasks to be executed.
Worker Queue - Priority queue that contains worker utilization info.
Running queue - It contains info about the currently running tasks and workers running the tasks.
Task Scheduler - It picks the optimal tasks/worker and instruct the chosen task worker to execute the job.
The resource manager works as follows -
The task scheduler gets the highest priority task from the task queue.
It gets the optimal task worker to run the task from the worker queue.
It instructs the chosen task worker to run the task.
The task scheduler binds the task/worker info and puts it in the running queue.
The task scheduler removes the job from the running queue once the job is done.
Task Workers.
Task workers runs the tasks which are defined in the DAG. Different task workers may run different tasks.
Temporary Storage.
Multiple storage system are used - It depends on the factor like data type, data size, access frequency, data life span.
Example - Metadata is frequently accessed by worker and the data size is small. Caching the metadata in memory is a good idea. The video and audio data we can put them in blob storage. Data in temporary storage is freed up once the corresponding video processing is complete.
Encoded Video.
It is the final output of the encoding pipeline. Example - funny_720p.mp4
System Optimization.
Optimizing the system including speed, safety and cost-saving.
Speed Optimization - Parallelize video Upload.
Uploading the video as an entire unit is inefficient. We can split the video into smaller chunks by GOP alignment.
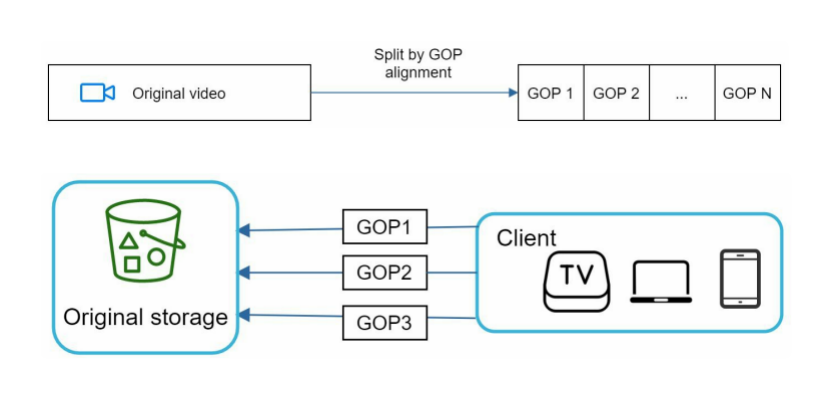
It allows fast resumable uploads when the previous upload failed. The job of splitting a video file by GOP can be implemented by the client to improve the upload speed.
Speed Optimization - Place upload centers close to users.
Improve the upload speed by setting up multiple upload centers across the globe. People in US can upload video in North America, China in Asian upload center. It can be achieved by CDN as upload centers.
Speed Optimization - Parallelism.
Achieving low latency need effort. Optimization - Use a loosely coupled system and enable high parallelism.
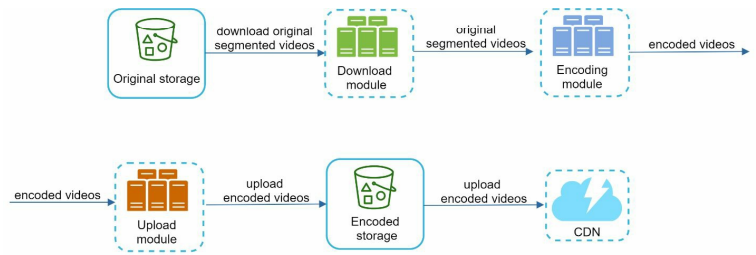
The output depends on the input of the previous step. This dependency makes the parallelism difficult.
To make the system more loosely coupled we introduced the message queue.
The message queue - encoding module does not need to wait for the output of the download module anymore. When there are events in message queue, the encoding module can execute the jobs in parallel.
Safety Optimization - pre-signed upload URL.
Safety is an imp aspect of the product. To ensure only authorized users upload video to the right location- we introduced a pre-signed URLs.
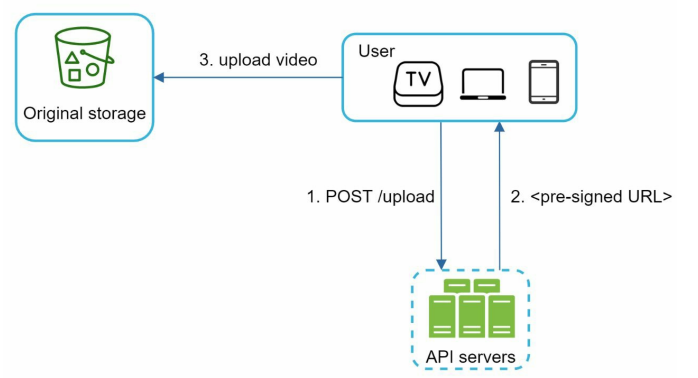
The upload flow is updated as follows.
1 - The client make Http request to the API server to fetch the pre-signed URL which gives the access permission to the object identified in the URL. The term pre-signed URL is used by uploading files to Amazon S3. Azure Blob storage support the same - “Shared Access Signature.”
2 - API servers respond with a pre-signed URL.
3 - Once the client receives the response it upload the video using the pre-signed URL.
Safety Optimization - Protect your videos.
To protect copyright - there are 3 safety options -
Digital rights Management DRM - 3 major DRM systems are Apple FairPlay, Google Widevine, Microsoft PlayReady.
AES - Encrypt a video and configure an authorization policy. The encrypted video will be decrypted upon playback. This ensure only authorized users can watch an encrypted video.
Visual Watermarking - Company logo or name.
Cost Saving Optimization.
CDN is imp and expensive when the data size is large.
Previous research show youtube video stream follow long-tail distribution - popular videos are accessed frequently and others have few or no viewers.
Based on the observation we can implement few optimization -
Only serve the most popular content from CDN and other video from video storage server.
Less popular content - no need to store many encoded video version. Short videos can be encoded on demand.
Some videos are popular only in certain region and no need t distribute these videos to other regions.
Building own CDN like Netflix and partner with ISP like Comcast, AT&T. ISP are located all around the world and close to users. By partnering with ISP we can improve the viewing experience and reduce bandwidth.
Error Handling.
To build highly fault tolerant system we must handle errors gracefully.
Recoverable Error - Video segment fails to transcode - retry and it continues to fail then return an error code to the client.
Non-recoverable - Malformed video format - the system stops the running tasks associated with the video and return the proper error code to the client.
Typical error for each system component.
Upload error - retry.
Split video error - Older version of client cannot split video by GOP alignmen - the entire video is passed to the server - the job of splitting video is done on the server side.
Transcoding error - retry.
Preprocessor error - regenerated DAG diagram.
DAG scheduler error - reschedule a task.
Resource manager queue down - use a replica.
Task worker down - retry the task on a new worker.
API server down - API servers are stateless so requests will be directed to a different API server.
Metadata cache server down - Data is replicated multiple times. One node down then still access other node to fetch data - bring up a new cache server.
Metadata db server down - Master is down - promote one slave to act as a new master. Slave is down - Use another slave for read and bring up another database server to replace the dead one.
Summary.
Additional points in case time permits-
Scale the API tier - API servers are stateless, it is easy to scale API tier horizontally.
Scale the database - Database replication and sharding.
Live Streaming - It is the process of how a video is recorded and broadcasted in real time. The system is not designed for live streaming. Live and non live streaming have the same work - uploading, encoding and streaming. The difference - Live streaming need higher latency requirement and need different streaming protocol. Live streaming has lower requirement for parallelism as small chunks of data are already processed in real time. It need different set of error handling. Any error handling takes too much time is not acceptable.
Video takedown - Videos violating copyright, illegal acts will be removed. Some can be discovered by the system during the upload process wile other might be discovered by the user flag.