Design NewsFeed System.
According to Facebook help page “News feed is a constantly updating list of stories in the middle of your homepage Newsfeed includes status, updates, photos, videos, links, app activity and likes from people page and group that you follow on Facebook.
It is similar to design Facebook newsfeed, Instagram feed, Twitter timeline.
Understand the problem.
Ask question to figure out what features to support.
Is it a mobile app or web app or both?
Both.
What are the imp features?
A user can publish a post and see her friends’ posts on the news feed page.
Is the news feed sorted by any reverse chronological order or any particular order such as topics course For instance post from your close friends have higher scores.
To keep this thing simple as of now that is assume that the feed is sorted based by the reverse chronological order.
Usercan have 5000 friends.
The system has 10 million DAU.
Feeds can contain image, media files, videos.
High Level Design.
The design is divided into two main parts - feed publishing and news feed building.
Feed Publishing - When user publishes a post the data is written to the cache and database. A post is populated to her friends news feed.
Newsfeed building - The news feed is billed by aggregating friends post in reverse chronological order.
APIs.
APIs are the primary way for clients to communicate with servers. It includes posting a status, retrieving news feed, adding friends. There are 2 imp APIs - feed publishing API and news feed retrieval API.
Feed publishing API.
HTTP POST request will be sent to the server.
POST v1/me/feed.
Param.
content - content is the text of the post.
auth_token - used to authenticate API requests.
NewsFeed Retrieval API.
GET v1/me/feed.
Param - auth_token - used to authentical API requests.
Feed Publishing.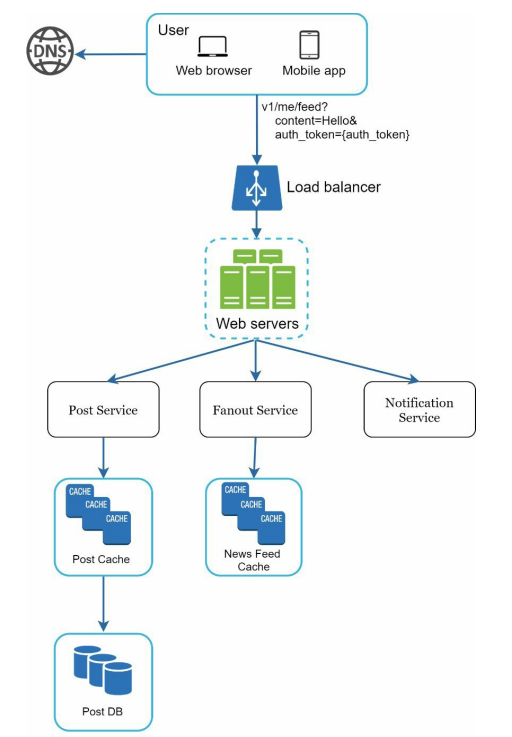
A user will view news feed on a browser or mobile app. A user will make a post with the content hello through API Post /v1/me/feed and body {”content”:”Hello”}. The load balancer will distribute to the Web Server and web servers will redirect the traffic to different internal services. Post service will persist the post into the database and cache. Fanout services will push new content to friends news feed. newsfeed data is stored in the cache for faster retrieval. The notification service informs friend that new content is available and send out a push notification.
NewsFeed Building.

v1/me/feed. the load balancer will return the traffic to the web servers and it will route the request to the newsfeed services. Thanes fit service fetches news feed from the cache and stored news feed ID needed to render the news feed.
Deep Dive.
Feed Publishing Deep Dive.
The main focus will be on two component web servers and fan out services.
Web servers - It communicates with client and it enforces authentication and rate limiting. User only signed up with valid auth_token are allowed to make post. The system limits the number of post user can make within a certain. It is important to prevent spam and abusive content.
Fanout - It is the process of delivering a post to all friends. There are two types of fanout models fanout on write (also called as push model) and fanout on read (also called as pull model).
Fanout on write - In this approach news feed is precomputed during write time. A new post is delivered to friends cache immediately after its published.
Pros - The news feed is generated in real-time and can be pushed to friends immediately. Fetching news feed is fast because the news feed is pre-computed during write time.
Cons - If a user has many friends, fetching the friend list and generating news feeds for all of them are slow and time consuming. It is called hotkey problem. For inactive users or those rarely log in, pre-computing news feeds waste computing resources.
Fanout on read - The news feed is generated during read time it is an on demand model. Recent posts are pulled when a user loads her home page.
Pros - For inactive users or those who rarely log in, fanout on read works better because it will not waste computing resources on them. Data is not pushed to friends so there is no hotkey problem.
Cons - Fetching the news feed is slow as the news feed is not pre-computed.
We will adapt in hybrid approach. Fetching the news feed fast is crucial so where will you go with the push model for majority of the user. The design will follow the pull model for the celebrity or user who has many friends or followers We let followers pull news content on demand to avoid system overload. Consistent hashing is useful technique to mitigate the hotkey problem as it helps to distribute requests or data more evenly.
The fan art service work is described in that high level image.
In step 1 Fetch friend id from the graph database graph database are suited for managing friend relationship and recommendations.
In step 2 get the front information from the user cache. the system then can philtre out the front based on the user settings Example if you mute someone her post will not be showed up on your news feed even though you are still friends. The other reason why posts may not show is that a user could selectively share information with specific friends or hide it from other people.
In step 3 get send friend list and new post id to the message queue and in step 4 Fanout worker fetch data from the message queue and stole newsfeed data in the newsfeed cache. You can think of the news feed cache as a <post_id, user_id> mapping table. Whenever a new post is made, it will be appended to the news feed table. The memory consumption can become very large if we store the entire user and post objects in the cache. Thus, only IDs are stored. To keep the memory size small, we set a configurable limit. The chance of a user scrolling through thousands of posts in news feed is slim. Most users are only interested in the latest content, so the cache miss rate is low.
In step 5 store <post_id, user_id > in news feed cache.
NewsFeed Retrieval Deep Dive.
Users send a request to retrieve the news feed. The request looks like v1/me/feed . The load balancer redistribute the request to server and it then calls news feed service to fetch news feed.
The newsfeed service gets a list of post IDs from the newsfeed cache. A users news feed is more than just a list of feed IDs. It contains username, profile pictures, content images and the entire details.
The newsfeed service fetches the complete user and post object from cache(user cache and post cache) to construct the fully hydrated news feed. the fully hydrated news feed is written in adjacent format back to the client for rendering.
Cache Architecture.
Cash is very important for the news feed system. we have divided the cash into 5 layers.
Newsfeed will store the id of the news feed. Content will store every post. Popular content is stored in hot cache. Social graph will store user relationship data. Action will store info about a user liked a profile, reply the profile or took other actions on the post. Counter will store the counter of like, reply, follower and following.
Summary.

Scaling the database - Vertical scaling or horizontal scaling, SQL vs NoSQL, master slave replication, read replicas, consistency model, database sharding.
Bonus points - Keep web tier stateless, cache data, multiple data centers, lose couple components with message queue, monitor key metrics like QPS during peak hours and latency when user refresh their news feed.