Design Google Drive.
Google drive a file storage and synchronization service that help to store document, photos, video, file.
Understand the requirement.
Imp feature - Upload and download file, file sync, notification.
Mobile app and web app.
File format can be any.
File in the storage must be encrypted.
File size limit - 10 GB or smaller.
User - 10M DAU.
Functional Requirement.
Add file, Download file. Sync file across multiple device. See file revision. Share file with a link.
Send notification when file edit, delete or shared.
Features not covered.
Google doc editing and collaboration.
Non-Functional Requirement.
Reliability - Data loss is unacceptable.
Fast sync speed.
Bandwidth usage - It take more network bandwidth then user will get bad experience in case they are on mobile plan.
Scalability - The system should handle high volume of data.
High availability - User should be able to use the system when some server are offline, slowed down or have unexpected network errors.
Estimation.
Application - 50 million signed up users and 10 million DAU.
User get 10 gb free space.
User upload 2 files per day - Average file size 500KB.
1:1 read to write ration.
Total space - 50 million*10GB = 500 Petabyte.
QPS for upload API - 10 million*2 upload/24hours/3600 seconds = 240.
Peak QPS = QPS *2 = 480.
High Level Design.
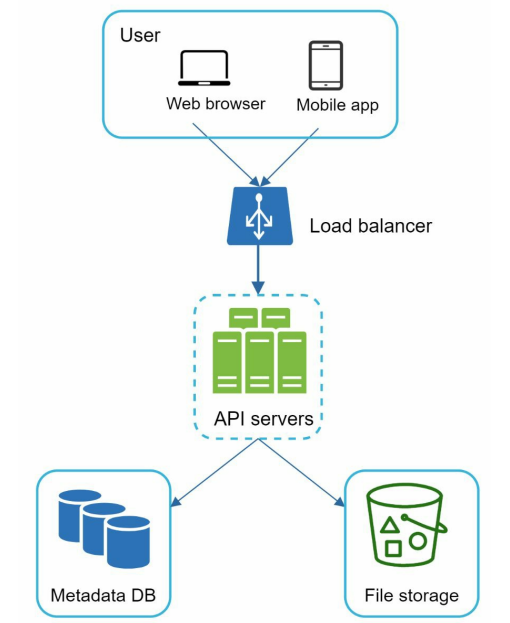
Starting with single server and then support million of users. It will include - Web server to upload and download files, A database to keep track of metadata like user data, login info, files info. A storage system to store files. Storage space 1TB to store files.
Apache webserver and Mysql db and a directory called drive/ as the root directory to store uploaded files. Under the drive/ directory there will be list of directory called namespace.
Each namespace contains all uploaded file for the user - each file and folder can be uniquely identified by joining the namespace and the relative path.
API
3 main API - upload, download and the get the file revision.
Upload the file.
2 types of upload simple upload(when file size is small), resumable upload(file size is large and chance of network interruption)
https://api.example.com/files/upload?uploadType=resumable - Param -uploadType - resumable and data - local file to be uploaded.
A resumable upload achieved by 3 step - Send the initial request to retrieve the resumable URL. Upload the data and monitor upload state. Upload disturbed resume the upload.
Download File from Google Drive
https://api.example.com/files/download - Param - path - download file path.
Example of Param - {"path":"/recipes/soup/best_soup.txt"}
Get file Revision.
https://api.example.com/files/list_revisions - Param - path - The path to the file to get the revision history and limit - The maximum number of revision to return.
API need user authentication and use Https. SSL Secure Socket Layer protects data transfer between the client and backend servers.
Storage space alert - 10Mb storage left in 1TB.
The first solution - shard the data so it is stored to multiple storage servers. Shard based on user_id. Example 4 servers then user_id%4 to store the data.
Netflix and Airbnb use Amazon S3 Amazon Simple storage Service. Amazon S3 is an object storage service that offers leading scalability, data availability, security and performance.
Understand S3 storage system and use store file in S3. Amazon S3 support same region and cross region replication. Redundant file are stored in multiple regions to guard against data loss and ensure availability. A bucket is like a folder in file system.
Additional parts to improve the application.
Load balancer - It distribute network traffic. A load balancer ensures evenly distributed traffic and if a web server goes down it will redistribute the traffic.
Web servers - With load balancer more web server can be added or removed depending on traffic load.
Metadata database - Move the database out of the server to avoid single point of failure. In the mean time set up data replication and sharding to meet the availability and scalability requirements.
File Storage - Amazon S3 s used for file storage. To ensure availability and durability files are replicated in two separate region.
Sync Conflict.
When 2 user try to modify the same file - one user changes are in the system other will override or sync with the final change. When multiple user is updating it become difficult to maintain.
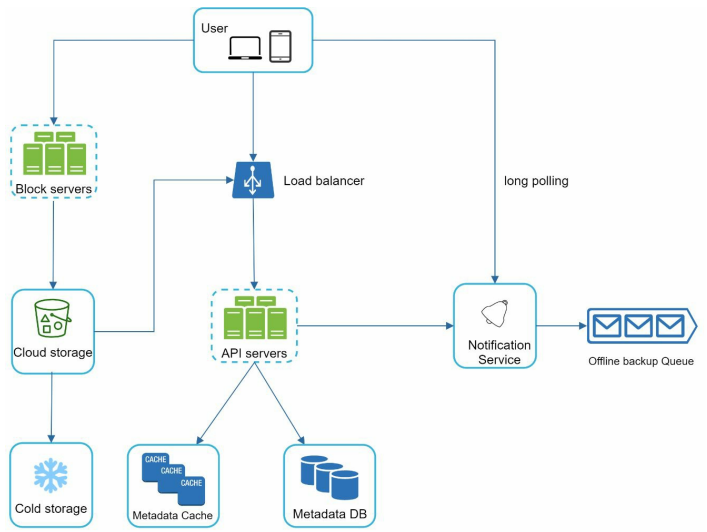
Block servers - It upload blocks to cloud storage. Block level storage - store data files on cloud-based environment. A file can be split into several block each with unique hash value stored in the metadata database. Each block is treated as an independent object and stored in our storage system. To reconstruct a file blocks are joined in a particular order. As for the block size we use Dropbox as a reference - minimal size of a block 4MB.
Cloud Storage - File split into smaller block and stored in cloud storage.
Cold Storage - Inactive data - file not accessed for a long time.
Load Balancer - It evenly distributes requests among API servers.
API servers - It is responsible for everything other than the uploading flow. API server are user for user authentication, managing profile, updating file metadata.
Metadata database - It stores metadata of users, files, block, version. Files are stored in cloud and metadata database only contain metadata.
Metadata cache - Some metadata are cached for fast retrieval.
Notification Service - It is a publisher and subscriber system that allows data to be transferred from notification service to client. In the system - notification service notifies relevant clints when a file is added/edited/removed so they can pull the latest change.
Offline backup queue - Client is offline and cannot pull the latest file change - it stores the info so changes will be synced when the client is offline.
Deep Dive.
Block server, Metadata database, Upload flow, download flow, notification service, save storage space and failure handling.
Block Server.
Large file updating regularly sending the entire file on every update consume bandwidth. Optimization to minimize the amount of network traffic being transmitted - Delta sync and Compression.
Delta sync - When file is modified, only modified blocks are synced instead of the entire file using a sync algorithm.
Compression - Applying compression on block can reduce the data size. Example - gzip and bzip2 are used to compress text files. Different compression algorithm are needed to compress images and videos.
In the system block server complete the heavy lifting work for uploading files. It process files passed from clients by splitting a file into blocks, compressing each blocks and encrypting it.
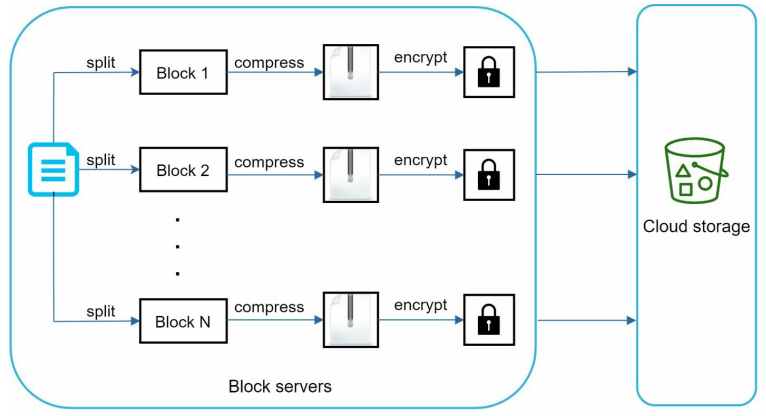
A file split to smaller block.
Each block compressed using compression algorithm.
To ensure security each block is encrypted before it is sent to cloud storage.
Block are uploaded to the cloud storage.
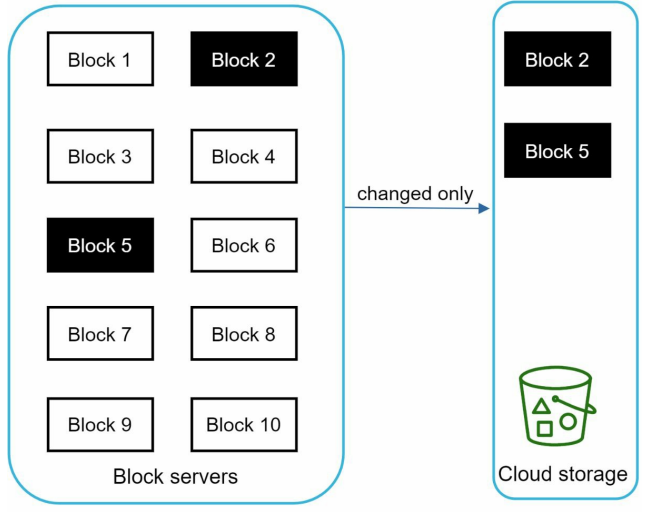
Delta Sync - modified blocks are transferred to cloud storage.
High Consistency Requirement.
System should not give different file to different user at same time. Memory cache adopt eventual consistency. To achieve strong consistency we must ensure - data in cache replicas and the master is consistent. Invalidate caches on database write to ensure cache and database hold the same value.
Strong consistency is easy to get from sql as it follow ACID property. Nosql do not support ACID property it needs to be added programmatically in synchronization logic. We will choose SQL.
Metadata Database.
It will include basic details.
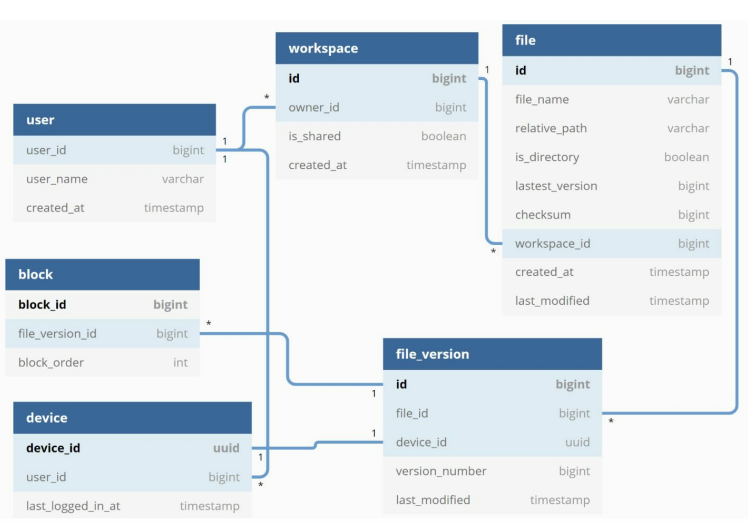
User - user detail like username, email.
Device - Push_id to send and receive mobile push notification. A user can have multiple device.
Namespace - A namespace is the root directory of a user.
File - Table store everything related to the latest file.
File_version - It store version history of the file. Existing rows are read-only to keep the integrity of the file revision history.
Block - It stores everything related to the file block. A file of any version can be reconstructed by joining the block in order.
Upload Flow.
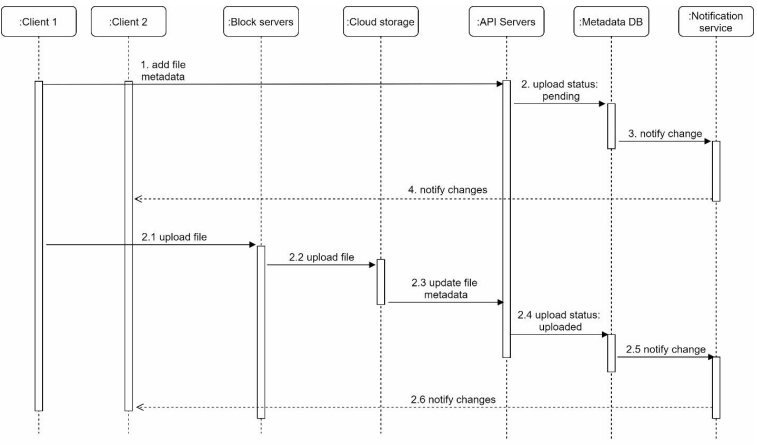
Add metadata and upload file to cloud storage request send at the same time - client 1.
Add file metadata.
Client 1 sends a request to add metadata of the new file.
Store the new file metadata in the db and change the file upload status to pending.
Notify the notification service that the new file is added. It notifies the clients that a file is uploaded.
Upload files to cloud storage.
Client 1 upload the content of the file to block servers.
The cloud storage triggers upload completion callback after the file is uploaded. The request is sent to API servers.
File status changed to uploaded in Metadata db.
Notify the notification service that the file status is changed to uploaded.
The notification service notifies relevant clients that a file is fully uploaded.
The work is same when the file is edited.
Download flow.
The download flow is triggered when a file is added or edited somewhere.
How a client know if a file is added or edited by another client?
There are 2 ways a client can know -
Client A is online when file changed by other and notification service will inform client A that changes are made and it needs to pull the latest data.
Client A is offline when a file is changed by another client data will be saved to the cache. When the offline client is online again, it pulls the latest change.
When the client know the file is changed - it first request metadata via API servers - then download blocks to construct the file.
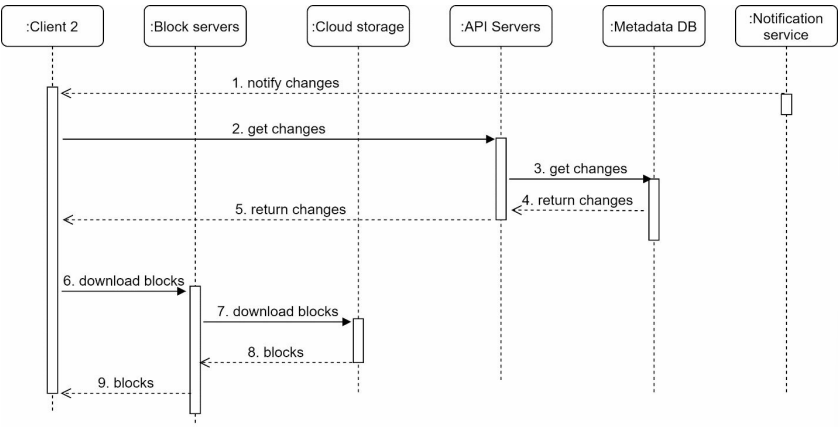
Notification service informs client 2 that a file is changed somewhere else.
Once client 2 know the new update is available it sends a request to fetch metadata.
API servers call metadata db to fetch metadata of the changes.
Metadata is returned to the API servers.
Once client receives the metadata it sends the request to block servers to download blocks.
Block servers first download blocks from cloud storage.
Cloud storage returns blocks to the block servers.
Client 2 downloads all the new blocks to reconstruct the file.
Notification Service.
To maintain consistency any update done locally should be informed to other clients. It allow data to be transferred to clients as events happens. The options - Long polling - Dropbox uses long polling. WebSockets - A persistent connection between the client and server and it is bi directional.
All the option are good but will opt for long polling. Main reason - Communication is not bidirectional. The servers sends information about the file changes to the client but not vice versa. Websocket is for real time bi directional communication like chat ap. In google drive, notifications are sent infrequently with no burst of data.
With long polling - each client establishes a long poll connection to the notification service. If change in file detected - the client will close the long poll and connect to the metadata server to download the latest change. After a response a received or connection timeout is reached a client immediately sends a new request to keep he connection open.
Save Storage Space.
To support file version history and ensure reliability, multiple version of same file are stored across multiple data centers. Storage space can be filled up quickly with frequent backups of all file revisions.
There are 3 techniques to reduce storage cost -
De-duplicate data blocks - Eliminate redundant block at the account level - Two blocks are identical if they have the same hash value.
Adopt new data backup strategy - There are 2 optimization - Set a limit and keep valuable version only.
Set a limit to the number of version to store - when the limit reached the oldest version will be replaced with the new one.
Keep valuable version - Saving heavily edited file meaning the file is saved over 1000 times within a short period. To avoid copies - we can limit the number of saved version and give more value to the recent change.
Cold Storage - Moving unused data to the cold storage. Cold data is the data that has not active for the last 6 months or years. Cold storage like Amazon S3 glacier is cheaper than S3.
Failure Handling.
Failure will happen in large scale system and we can adopt strategies to address the failure.
Load Balancer Failure - If one load balancer is failed then the second one should be active and get the traffic. Load balancer usually monitors each other using heartbeat and it is considered failed if they does not send heartbeat.
Block server failure - One fail then other picks up unfinished or pending jobs.
Cloud Storage Failure - S3 buckets are replicated multiple times in different regions. If files not available in one region then they can fetch from different region.
API server Failure - It is a stateless service. One server fails - traffic redirects to other API servers by the load balancer.
Metadata cache failure - Metadata cache server are replicated multiple times. If one node goes down - you can still access to other nodes to fetch dat. We will bring up a new cache server to replace the failed one.
Metadata DB failure - Master down - Promote one of the slave to act as new master. Slave down - Use another slave for read operation and bring another database server to replace the failed one.
Notification service Failure - Every online user keeps a long poll connection with the notification server. Each server connected to many users. Dropbox once mentioned that over 1 million connections are open per machine. If one server goes down all long poll are lost so clients must reconnect to different server. One server can maintain many connection - it cannot reconnect all the lost connections at once. Reconnecting with all lost clients is slow process.
Offline Backup Queue Failure - Queue are replicate multiple times. Of one fails consumers of the queue may need to resubscribe to the backup queue.
Summary.
It is a combination of strong consistency, low network bandwidth and fast sync.
Timer permits discuss with different design -
Example - Upload directly to cloud storage and not using block storage - it will be faster as file only need to be transferred once to the storage. Drawbacks - the compression logic must be implemented on platform. It is error prone and need lot of engineering input. In out design all are implemented in centralized place - block servers. As a client can easily be hacked implementing encrypting logic on the client side is not ideal.
Example - Another modification in the system in moving the online/offline logic to a separate service - by moving out of notification service, the online/offline functionality can be easily integrated by other services.