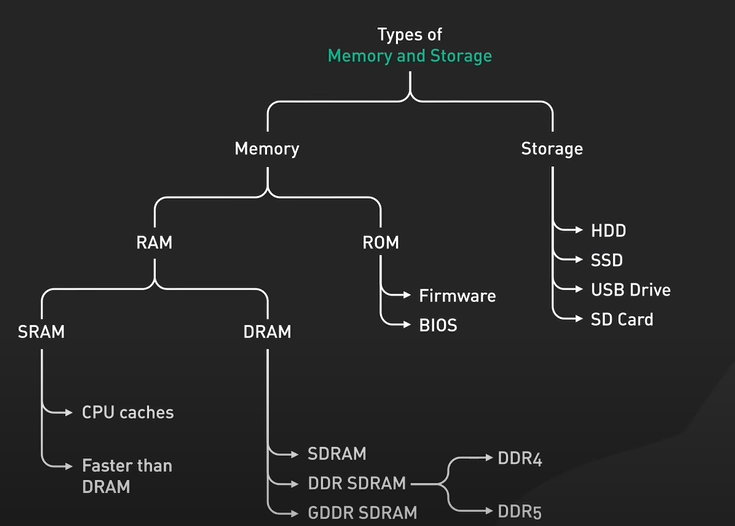
Memory And Storage System
RAM.
- Stores data temporarily while your computer is running.
- It’s fast and flexible, juggling all the programs we’re running at any given moment.
- RAM is volatile, meaning it loses its stored data when the power is turned off.
ROM.
- Retains data even when the power is off.
- It’s non-volatile and used to store essential information, like firmware and the BIOS, that your computer needs to boot up.
Different types of RAM
SRAM or Static Random Access Memory - Fast and expensive type of RAM used in high-speed applications like CPU caches, where quick access time is crucial.
DRAM or Dynamic Random Access Memory - Slower and cheaper than SRAM. It needs to be constantly refreshed to retain data, making it more high-maintenance.
There are many types of DRAM, including FPM DRAM, EDO DRAM, SDRAM, and DDR SDRAM with each generation bringing faster speeds and increased efficiency.
Many are obsolete, and the common types of DRAM
in the market today are DDR variants, like DDR4, DDR5.
GDDR - It is a specialized type of DRAM optimized for faster data transfer rate, which the GPU needs for its massive parallel processing.
GDDR6 is the most widely used today.
Essential roles of ROM: Firmware and BIOS!
Firmware - Type of software stored in ROM that
controls how hardware devices communicate with each other.
BIOS, or Basic Input/Output System - The first software your computer runs when you power it up.
It’s responsible for starting your computer, initializing hardware components, and handing control over to the operating system.
Hard Disk Drives and Solid State Drives.
Hard Disk Drives or HDDs.
They store data on spinning magnetic disks and are known
for their large storage capacities at a low price.
Solid State Drives or SSDs.
It uses NAND-based flash memory, providing faster data access, reduced power consumption, and increased durability compared to HDDs, but come at a higher price.
NVMe or Non-Volatile Memory Express.
A high-performance interface for SSDs that connects directly to the CPU via PCIe lanes.
This allows for lower latency and significantly faster data transfer rates compared to SATA-based SSDs.
Flash Drives and SD Cards!
Flash Drives or USB drives or thumb drives - Small, plug-and-play devices you can use with any USB port. They’re easy to use and perfect for transferring files between computers.
SD Cards - Commonly found in cameras and smartphones. They can store thousands of files. SD cards come in three main physical sizes: SD, microSD, and miniSD.