Handling Distributed Transaction
Handling Distributed Transaction.
A set of operations which need to be performed or simply say goroup of tasks which need to be performed against the db.
It has 4 parts. - Design Course.
Atomicity - All operations in a single transaction should e success or all should fail.
Consistency - Db should be in consistent state before and after the transaction.
Isolation - More than one transaction that is running concurrently, appears to be serialized.
Durability - After transaction successfully completed even if db fails data should not get lost.
In one db when we do any work then we put lock and then do the next work.
What will happen when there are two db and so one table update and other should also update. When the other table did not completed then the task is remove from the other table but how will the first table know about the task not fulfilled.
How do we handle transaction in distributed system.
2 Phase Commit.
3 Phase Commit.
SAGA Pattern.
2 Phase Commit.
There are 2 phases in the protocol - Voting or Prepare phase. Decision or commit phase.
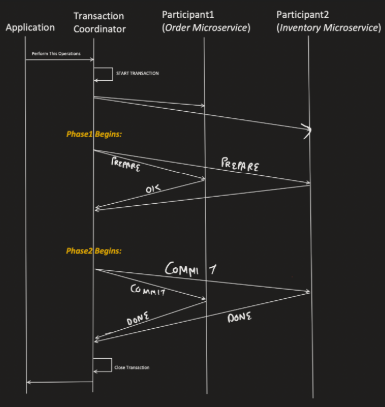
Transaction coordinator will connect with the participants.
Say the message is send to order and inventory db. When the message come then there is a lock with the order and the inventory database and they made the changes and has not committed the changes.
In phase 1 the transaction coordinator will ask the participants if they are prepare to commit and made the changes then it will send ok.
In phase 2 when coordinator gets the message that all articipants are prepared then it will take the decision and ask to commit.
The participants all all component has a log file and all are updated in the file.
When the prepare message fails to send or message as no then abort the order.
OK message lost - Abort the order.
The commit message lost - When the commit message is lost then the participant is in block state and need to wait for the input like the message is block or commit.
Participant cannot take any step by itself. It needs to wait.
3 Phase.
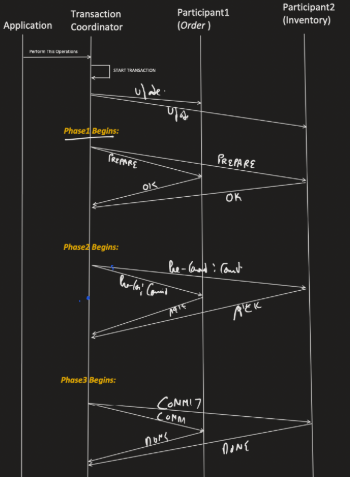
Non blocking. When the coodinator makes the decision that it will commit then it send the message to the participants so that it does not wait. The commit order is not send it only send the order message.
When the commit message fails then the participants communicate with each other when no one get any commit message then they abort.
SAGA Pattern.
When there is long transaction like one participants and then another. It is not lock to all the participants and only one db is lock and it will send the message to the next participants.
When one participants is not completed it will roll back the changes.