Kafka The Definitive Guide - 14 Stream Processing.
Kafka was initially seen as a message bus - deliver streams of message without any processing and transformation.
Steam Processing systems - Apache Storm, Spark, Flink, Samza are build with Kafka. Starting from 0.10.0 Kafka data stream using stream processing library as part of its client libraries Kafka Stream. It allows to consume, process and produce events using Kafka without any external framework.
Stream Processing.
Data Stream / Event Stream / Streaming Data - An abstraction representation an unbounded dataset. Unbounded means growing as more data are coming. Attributes od event stream model -
Unbounded nature.
Event streams are in order - It is one of the difference between an event stream and db table - record in db are not considered to be in unordered and order by is not part of relational model it is added to assist in reporting.
Immutable data records - Event once occurred can never be modified. The difference between db and data stream - delete or update record the data in the table and all are additional data. binlog, WALs, or redo logs when insert data and delete it, the table will not include the record but the redo log will contain 2 record - insert and delete.
Event Streams are replayable - non replayable stream TCP(packets streaming through socket are non replayable). Business requirement to replay the stream occurred months or year back.
The data in the event stream or data stream can be small or large XML file with multiple headers, unstructured key-value or semistructures JSON or structured Avro or ProtoBuf.
Stream Processing refers to the ongoing processing of one or more event stream.
Request-Response.
Low Latency.
Response time ranging from submilliseconds to few milliseconds. App send the request and wait for the response.
In db it is refered as OLTP.
Batch Processing.
High latency or high throughput.
Procesing time is like every day fixed time, once in an hour.
Stream Processing.
Continuous and non blocking option.
Network activity, tracking delivery of the package all are the example of continuous and non blocking processing.
Stream Processing is very similar to data processing - receive the data, do some modifycation(transformation, aggregates, enrichments) and place the result. There are some key concept that are different in stream processing and data processing.
Topology - A processing topology starts with one or more source stream that are passed through a graph of stream processors(steps appled to the event to transform like group by, count, filter, left-join) connected through event stream until result are written to sink.
Time - Stream application perform operations on time window. Example - Application calculating the moving 5 mins average of stock price. It refers to the following notion of time -
Event Time - The time a measurement was taken. Kafka automatically add the current time to producer records at the time they are created. In case Kafka record the created time based on the data on the db record after the event occured then we can add additional field of event time in the record to track the exact event occurred time.
Log Append Time - The event arrived at the Kafka broker and was stored there Ingestion time
Processing Time - Time SP app receives the event. The time can be ms hours or days after the event occurred. There can be different time for the same event depending on the time the sp application read the event. This time is not reliable.
Kafka Stream assign time to each event based on TimestampExtractor interface and user can implement with own logic. They can use 3 time semantics or diff choice of timestamp. Kafka stream writes output to the Kafka topic and assign tiemstamp to each event based on the rules -
When Output Record (OR) maps directly to the Input Record (IR) the OR will use the same timestamp of the Input.
When the OR is the result of some aggregation the OR will be the maximum timestamp used in the aggregation.
When the OR is a result of joining two streams the OR will be the largest of the two record being joined. When a stream and the able are joined the timestamp from the stream record is used.
When the OR was generated bu the Kafka Stream function that generates data in a specific regardless of input like punctuate() the Output time depend on the current internal time of the stream processing app.
When using the Kafka Stream lower level processing API rather tha DSL, Kafka Stream includes API for manipulating the timestamps and developer can add the business logic.
The entire application should have a single timezone.
State - The processing of one event at a time is very easy liek stream of transaction and mail to the customer with more than $1000 order then simple using Kafka consumer and SMTP library. SP becomes interesting when there are multiple task like counting number of event by type, moving average, joining two stream to create enrich stream of information. We need to more than one event like how many event of each type in an hour - This information is called State.
One tempting way to keep in variable like hashmap and store the mobing count - not good when application is stoped the state is lost. Persist the most latest state and recover it when restarting the application. SP refers to several types of state -
Local Internal State - Accessible only by a specific instance of the sp application. Maintained with an embedded, in-memory da running within the application. Adv - fast. Dis-adv - Limited amount of memory. As a result, the design pattern in sp focus on ways to partition the data into substreams that can be preocessed using small amount of local state.
External State - Maintained in external data store like Cassandra.Adv - Unlimited size and can be accessed from multiple instances of the application or different application. Dis-adv - Extra Latency and availability - application need to handl the possibility that external system not required. Apps try to avoid deal with external store or limit the latency by caching in local state and communicating with the external store rarely.
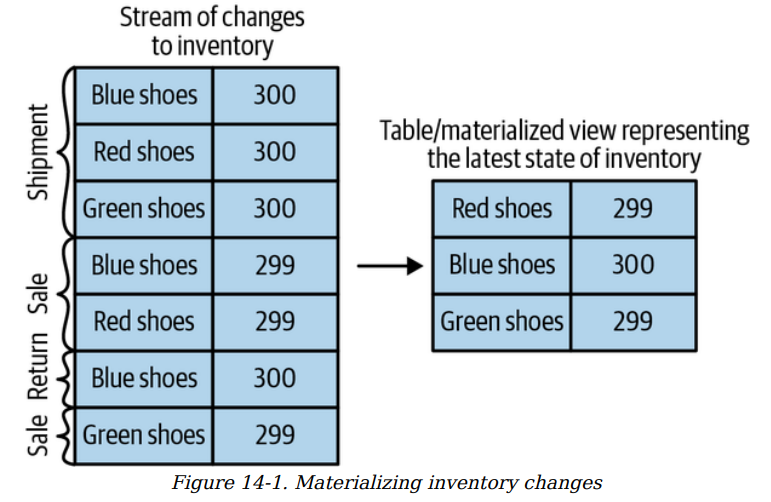
Stream Table Duality - Db Table (collection of record identified with Primary Key and contain set of attributed defined by the schema). Table record can be changed like contact_detail table will contain the latest contact of the person unless it has a history table. Schema contains the history and it contains the change. Requirement can be different sometime interested to see the final data and sometimes interested to see what changed the data. Db need to store all the CRUD details to show the change. Most Db offer Change Data Capture CDC to capture the changes and kafka connector can pipe those changes into kafka where they will be available for stream processing.
Convert stream to table need to apply all the changes that stream contains - called Materializing the stream. In store the stream will contain all the data and to get the final data we need to materialize the view.
Time Windows - Operating on slice of time - moving averahe, top product sold this week. Join operation on two stream are also windowed - join events at the same time.
Calculating moving average we need to know -
Size of the window - Larger window are smoother but it lag and price increases then it will take longer to show the data. Kafka Stream also include session window the size defined by period of inactivity. Event that arrive with gaps smaller than the defined session gap belong to same session. A gap in arrivals will define a new session and all events arriving after the gap but before the next gap belong to the new session.
How often the window move?(advance interval) - Window where the size is a fixed time interval hopping window When the advance interval is equal to the window size it is called tumbling window.
How long the window remains updatable (grace period) - The average for 5 mins say one dta at 2 mins come after an hour what should be done update the result? leave the new data? There is a period of time
Kafka Stream Architecture.
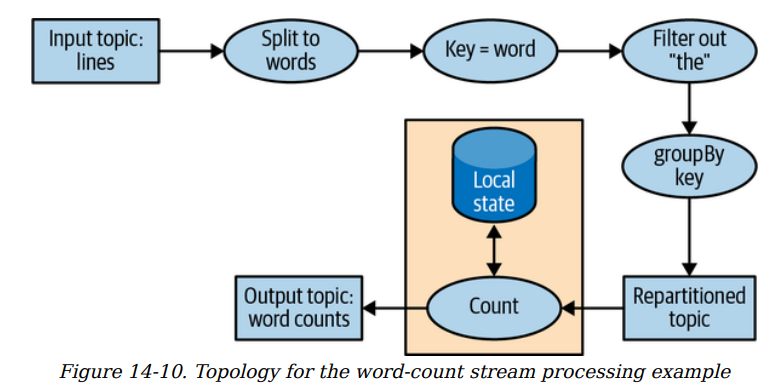
Topology
Summary.
Explain Stream Processing, definition and attribute.
Comparing with other programming paradigm.
Imp sp (Stream Processing) concept and 3 examples with Kafka Stream.
Kafka Stream architecture.
SP use cases and compare different Stream Processing frameworks.