Kafka The Definitive Guide - 01 Introduction.
Kafka - Introduction.
Fast data movemenet makes the application more responsive.
Pub/Sub system have a broker a central point it publishes the message.
Direct communication will make it more difficult to maintain.
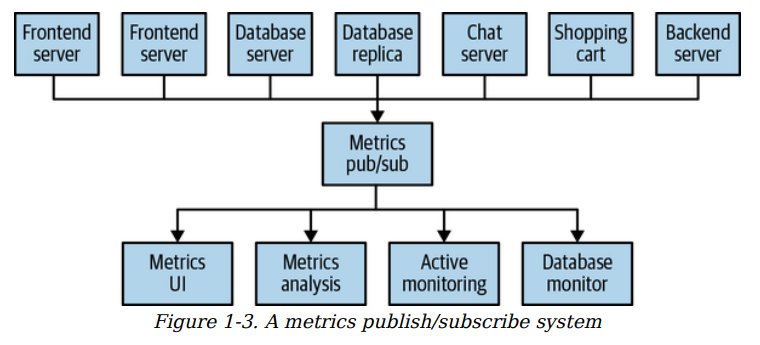
There should be a single application that act as a broker. Multiple user is working in multiple part like logs, tracking user activity and individual pub sub for the message is still good but there will be more bugs.
A centralized single system is imporatant - Introduced Kafka.
Kafka was designed as a publish/subscribe messaging system also called distributed commit log or distributed streaming platform.
The unit of data within Kafka is called message. A message is simple an array of byte it can contain key. Key is used to store the data in the partition. It generate a consistent hasg of the key and thenn select the partition number by doing hash modulo of the total number of partitions in the topic. It ensures message same key will be in same partition when partition count does not change.
Messages are written into Kafka in batches. A batch is a collection of message all produce to the same topic and partition. There is a trade-off between trouhput and latency the larger the batch more message process but the longer it takes an individual message to propagate. High latency and high throughput. Batches are compressed to improve transfer and storage cost.
Responsive target is low latency and high throughput.
Messages are byte array and additional structure are added like the schema like JSON or XML. They lack type handling and compatibilit between schema version. Best - Apache Avro.
A serialization framework by Hadoop provides a compact serialization format schemas that are separate from message payload and that do not require code to be generated when they change and strong dta typing and schema evolution with forward and backward compatibility.
When the data format is coupled then application subscribed need to change to handle new data format. Making well defined schema and storing in common repositories it will make Kafka understood the message without coordinations.
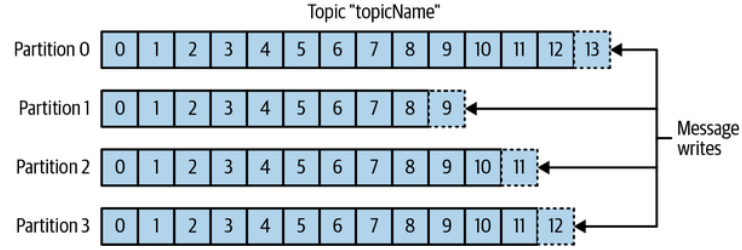
Message are categorized into topics. Topic - db table. Topics are broken down to partitions. Kafka - commit log and Partition - single log.
Messages are written in append-only way and read from beginning to end.
Partition is the way Kafka provides redundancies and scalability.
Each partition can be hosted on a different server meaning a single topic can scale horizontally acorss multiple server.
Partition can be replicated and different server will store a copy of the same partition.