OOPS
Java OOPS.
| Procedural Programming | Object Oriented Programming. |
|---|---|
| Program is divided into parts called functions. | Program is divided into Objects. |
| Does not provide proper way to hide data, gives importance to function and data move freely. | It does provide proper way to hide the data. |
| Overloading, Inheritance is not possible. | Overloading, Inheritance is possible. |
| C | Java |
Abstraction.
It hides the internal implementation and shows only essential functionality to the user. It can be achieved through interface and abstract class.
Example - Car and break the functionality is not known.
Encapsulation.
It bundles the data and the code working on the data in a single unit. It is also known as Data Hiding.
Overview.
Java is a Object oriented language and it is WORA - Write Once and Run Anywhere.
JDK - has JRE - has JVM.
Java Program is platform independent and it compiles to bytecode (.class file is generated) and then JVM converts to the machine code and runs by CPU.
JVM is machine dependent installed for mac or window and it can convert the java program as it has JIT(Just In Time) compiler.
JRE - has the class library and JVM.
Why there is only one public class in java and main class is inside the public class.
Jvm calls the main method and it calls by the class and the method is static.
It directly calls A.main().
Only one public class as when there will be more public class how JVM will know that which class has the main method. The public class should be the name of the file.
UML (Unified Modeling Language) diagram are the representation of the Object Oriented Concepts. It identifies the objects of a system. It defines relationships between objects. It establishes an interface of each object.
UML is represented in two categories.
Structural Diagram - Class diagram, Object diagram, Package diagram, Component diagram, Composite structure diagram, Deployment diagram, Profile Diagram.
Behavioral Diagram - Use case diagram, Activity diagram, Sequence diagram, State diagram, Communication diagram, Interaction overview diagram, Interaction overview diagram.
Class diagram - Describe structure and behavior in the use cases. It shows connection between teh entities. It shows the attribute and operation of the class.
Use Case diagram - Describe a set of user scenarios or actors. It illustrates the functionality provided by the system.
The actors on the left and right side and the use cases in circle shape.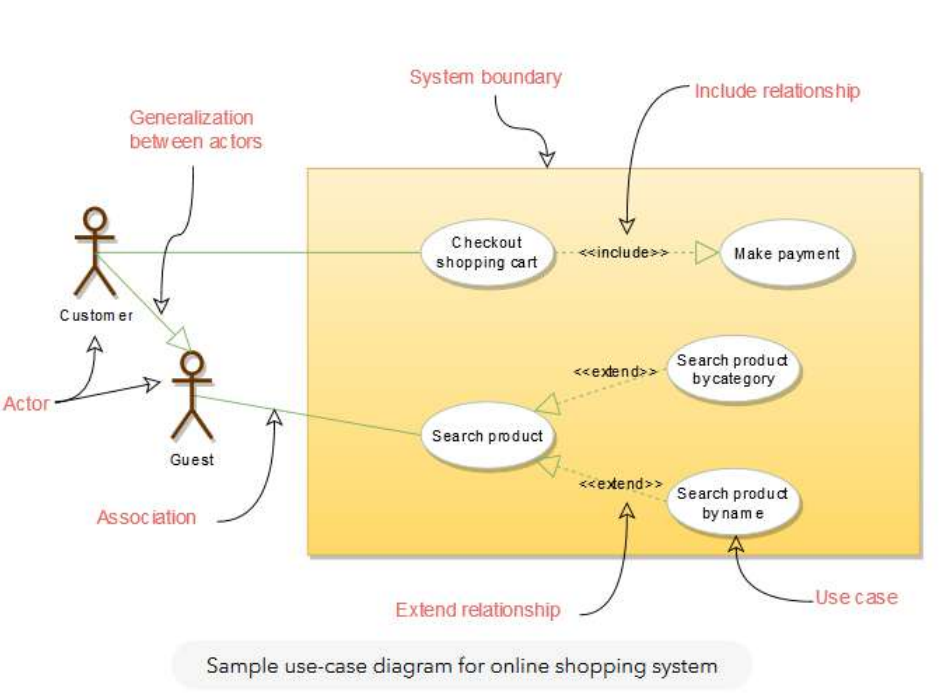
Activity diagram - Used to model the functional flow of control between two or more class object.
Sequence diagram - Sequence diagrams describes interactions among classes in terms of an exchange of messages over time.
There are different types of relationship in a class.
Association.
Relationship between 2 different object.
Both the class know about each other. Example the Pilot and FlightInsurance both class know each other exists.
Aggregation - Both object can survive individually, means ending of one object will not end another object.
Composition - Ending of one object will end another object.
Multiplicity.
- Indicates number of instance of the class is there in the relationship.
- Example One FlightInstance will have two Pilots, while a Pilot can have many FlightInstances.
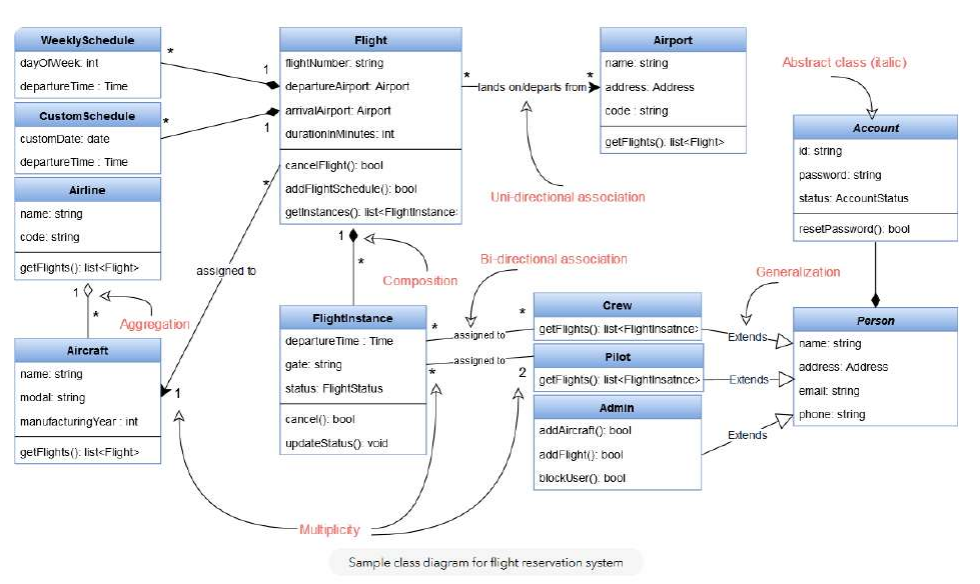
Sample Class Diagram.
Aggregation
- Special type of Association.
- It is a
WHOLE to its PARTrelationship. - The lifecycle of a
PART classis independent of theWHOLE classlifecycle. - Aggregation implies a relationship where the child can exist independently of the parent. Example - Aircraft can exist without Airline.
Composition
- It is a type of aggregation where the child class’s instance lifecycle is dependent on the parent class’s instance lifecycle. A stronger “whole-part” relationship where the part cannot exist without the whole. If the container object is destroyed, the contained objects are also destroyed. Example: A car “has” an engine, and if the car is destroyed, so is the engine.
- Child cannot exist without parents.
- WeeklySchedule is composed in Flight which means when Flight lifecycle ends, WeeklySchedule gets destroyed automatically.
IS-A Relationship. Achieved through Inheritance. Dog is a animal. Inheritance form an IS-A relation between its parent child class.
HAS-A Relationship. Whenever an object is used in other class. Relationship should be one to one, one to mane, many to many. School has Student. Bike has Engine. School has Class.