Git Guide
Detailed Explanation will go here. Basic Command will be in https://github.com/Suchismita-Deb/Github-Guide
git init.
git init will create the config file and it is for the local configuration. It will not be pushed in the server.
When we write git init it creates the .git folder and the config file looks like.
[core]
repositoryformatversion = 0
filemode = false
bare = false
logallrefupdates = true
symlinks = false
ignorecase = true
git remote add
When we write git remote add origin https://github.com/Suchismita-Deb/x.git then it creates nr remote in config file.
[remote "origin"]
url = https://github.com/Suchismita-Deb/x.git
fetch = +refs/heads/*:refs/remotes/origin/*
git remote set-url.
# If the project is already a git project and you want to set github repo to the existing project.
# If you rename the project then you can also set from here.
git remote set-url <remote_name> <remote_url>
git remote set-url origin https://github.com/Suchismita-Deb/x1.git
This will change in the config file.
git branch.
The more we push and pull from different branch and create new branch then it will be created in the config file.
[branch "test"]
remote = origin
merge = refs/heads/test
Delete any branch in git.
When we do not need the branch or the details we can delete from the config file. First checkout to main or any other branch then delete the branch.
# To delete a fully merged branch (with prompt if not fully merged)
git branch -d branch_name
# To force delete a branch, including unmerged changes
git branch -D branch_name
This will delete the details from the config file.
Cleaning config file.
git remote prune origin && git repack && git prune-packed && git reflog expire --expire=1.month.ago && git gc --aggressive
git prune This command removes any local references to remote branches that no longer exist on the remote repository named “origin”. It cleans up your local tracking branches that are no longer relevant.
git repack This command packs loose objects in the repository into pack files, optimizing the storage and performance of the repository by compressing objects.
git prune-packed This removes redundant pack files, cleaning up any pack files that are no longer necessary after repacking.
git reflog expire --expire=1.month.ago This command expires old entries in the reflog that are older than one month. The reflog is a reference log that stores a history of where the tips of branches were in the past.
git gc --aggressive This command triggers the garbage collection process in Git. It optimizes the repository by cleaning up unnecessary files and optimizing the repository’s storage.
Revert back the changes already commit and push in the server.
For personal project where only I am contributing.
git reset HEAD~1 This will revert back the changes. The changes will be there in the stage area.
git reset --hard HEAD~1 This will remove the changes from the stage area.
git push -f origin main This will push the changes andwe have to force push the changes. Now the repo will have the file which was like the previous commit.
If we need to do revert 5 commit then we need to run the first command 5 time.
Removing the file or folder from the server.
git rm --cached <file/folder_path> - Remove a file from the staging area (also known as the index), while keeping it in your working directory git rm --cached build/*
Then we can push to the main. git push origin master
In the blog when make one folder change and all I have to create a folder and make the page. With the move directory it is giving 404 error.
- In order to make the page hide
draft = trueand make the folder and add the pages. Like the one for design pattern I had a separate folder then I had to move to the system design folder. - Direct moving the folder is giving the error so created noe pages and then make the old folder pages hide.
Git tags.
Tagging in git refers to creating specific points in history for your repository/data.
It is done to mark the release points for a stable version of the code.
When you want to create a historic point for your code/data that you can refer at any future time.
Checkout to the branch and then create a tag.
git tag <tagName> like git tag v1.0
Create a annotated tag.
get tag -a <tagName> -m <Version1 of ..."> like git tag -a v1.1 -m "tag for release 1"
In annotated tag the message can be stored and it is stored as an object in git.
Display the goit tag.
git tag - It will show the tag name.
git show <tagName> - It will show the details of the tag.
git tag -l "v1.*" - It will show all the tag starting with v1.
When we push tag to the remote then in the github we can see the releases.
git push origin v1.0 - Push the git tag to remote.
git push --tags - Push all teh tags to remote.
git tag -d v1.0 - Delete teh tag from local.
git push origin -d v1.0 - Delete the tag from origin.
Rebase in Git.
When we make a feature branch and then make a commit and when merge it will create a separate flow and then merge the branch to the main.
When we use rebase then it will directly come on top of the main.
You are in feature branch and the main and the feature branch are latest change then rebase the feature branch with the main branch git checkout feature then rebase git rebase main.
Checkout the main and rebase the main teh feature git checkout main then git rebase master then we have to do git push.
CherryPick.
Get the commit from there the branch and use it.
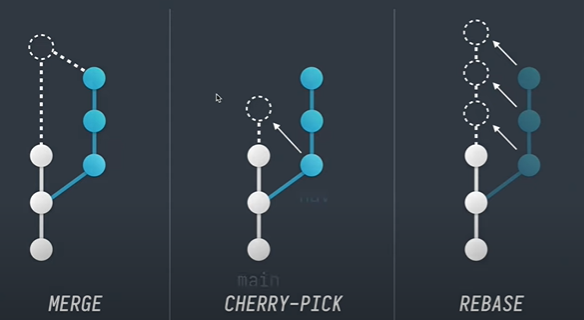
git log - Show all the commit and the code.
git log branchName --oneline - Show all the commit in the branch.
Checkout to the branch where we will add the commit.
git checkout main. Pick the commit git cherry-pick <hashcode>
Blog page.
The paper theme is the submodule. When I clone the project the url was set to the original person url. When making any update in the paper module no access permission.
[submodule "themes/paper"]
path = themes/paper
url = https://github.com/nanxiaobei/hugo-paper
[submodule "themes/hugo-paper"]
url = https://github.com/Suchismita-Deb/hugo-paper.git
I had to first remove the submodule and then fork the repo and point the repo to the new repo.
# Deinitialize the submodule.
git submodule deinit -f themes/paper
# Remove the submodule entry from the Git index.
git rm -rf themes/paper
# Clean up the .git/modules directory
rm -rf .git/modules/themes/paper
# Adding the new sub module
git submodule add https://github.com/Suchismita-Deb/hugo-paper.git themes/paper
# Initialize and update the submodule.
git submodule update --init --recursive
# Commit and push the change and add the .gitmodule change.
git add .gitmodules themes/paper
git commit -m "Re-added paper theme submodule under my fork"
git push origin main
The .gitmodule should look like this.
[submodule "themes/paper"]
path = themes/paper
url = https://github.com/Suchismita-Deb/hugo-paper
Git SubModule.
In Blog when large file entered into the
git config --global user.email - It will see the username in the github.
Making contribution in any other account then set the user name and email in the local. In terminal set the value and then commit.
git config user.name "Suchismita-Deb"
git config user.email "su2000@gmail.com"