JBoss Fundamental
JBoss.
Web Server and Application Server.
Static content in a page is stored in the Web server like the text, image.
Dynamic content are stored in application Server. We need servlet and JSP.
Application server is divided into two parts - small scale server and full scale server.
Web server - Apache Http server, Tomcat, Weblogic, web experience and jboss.
Apache Http Server - It is a web server. It has the capability only of teh static content.
Tomcat - Small scale application server. It is used for the static content and alos used for the dyncmic content in servlet and jsp.
Jboss - full application server.
ejb - weblogic, jboss, websphere.
JBoss, EAP, Wildfly - Different version of JBoss application server.
JBoss is a free and open source java based application server under GNU Lesser General Public License (LGPL).
LGPL is a free software licensing which allows users organization and companies to use and update them and even release as their own proprietary software but source code availbility is one the major condition under LGPL.
It was developed by JBoss and now a division of Red Hat. There are two parts of JBoss - Open Source Community Edition (JBossAs or JBOss - Now Wildfly) and Red Hat Enterprise Edition (JBoss EAP)
Red Hat JBoss EAP 7.3
History - Mark Fleury founded in 1999 as JBoss Group LLC. JBOSS - Java Bean Open Source Software. JBOss Group LLC became JBoss Inc in 2004. First Release - 0.0.4 (No pecific compliance to J2EE). First J2EE complaiance release - 4 with JDK 1.4
Complete J2EE compliance release - 7.1 JBoss B is renamed to Wildfly.
Small application srever with which he create a component and host application.
JBoss is community and people may change something and stop any part and it is maintained by community not reliable. RedHat took JBoss and now it is EAP Red Hat.
Components of JBoss.
Wildfly core 10.1.2 - Inside EAP there is application server. It has the version.
Undertow - Web server packaged inside JBoss.
JGroup, Infinispan, Iron Jacamar - are component helpd i clusing in JBoss.
Narayana(Trxn), Active MQ Artemis, JBoss Logging, HAL (admin console), JBoss Security, Picketbox(vault), Netty (Http protocol connector)
Operation Model - Standalone and Domain Mode.
Core component of JBoss.
Domain and Host controller.
Deploying and operating mode of JBoss.
Development and Testing.
Standalone Server.
The standalone server operating mode represents running JBoss as a single server instance. A standalone server instance is an independent process.
We can launch multiple instances of the standalone servers in case multi server configuration is desired.
We need to manage each of the server individually.
We will need to deploy the application on each server individually.
Each JBoss server has its own configuration.
Each JBoss standalone server has its own admin console and is managed independently.
Production - High Availability architecture.
Managed Domain.
The Managed domain operating mode allows for the management of multiple JBoss instances from a single control point.
The JBoss “Domain” mode differs from traditional standalone mode and allows you to deploy and manage JBoss instances in a multi server topology.
All changes will be shown in each instance of JBoss.
A managed domain spans over multiple hosts with centralized administration and management policies.
Each host that runs in domain mode can contain several server instances that belong to one domain.
Central control of multiple servers.
Central configuration for multiple servers.
JBoss - JavaBeans Open Source Software.
In domain mode there are two thing domain controller and host controller.
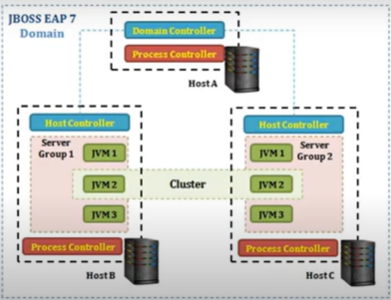
The master controller is the place contains all configuration is Domain controller.
The independent other server in the same domain is host controller. Inside the host controller there will be some manage server.
Core Component - Domain and host controller, server group and profiles.
Configuration
Configuration Files and Structure JBoss configurations are defined in XML and property files located within the server’s directory structure:
Standalone Mode: Path: $JBOSS_HOME/standalone/configuration/
Key file: standalone.xml
Domain Mode:
Path: $JBOSS_HOME/domain/configuration/
Key files:
domain.xml (domain-level settings)
host.xml (host-specific settings)
These XML files define:
Subsystems (e.g., logging, data sources, deployments). Security settings. Networking and port configurations.
Modes of Operation JBoss operates in two modes:
Standalone Mode: For single-server setups. Suitable for development and simple deployments. Domain Mode: For managing multiple servers from a central control point.
Subsystems Subsystems define specific functionalities like:
Datasources: Configuration for database connections. Example
Ports Configured in the socket-binding-group element. Example (Standalone Mode): xml Copy code c. Deployments Defines application deployments, such as WAR or EAR files:
Deployments can be specified in the standalone.xml or managed dynamically via the management console or CLI. d. JVM Options Java Virtual Machine settings (e.g., heap size) are configured in the script:
Standalone Mode: $JBOSS_HOME/bin/standalone.conf Domain Mode: $JBOSS_HOME/bin/domain.conf Example:
JAVA_OPTS="-Xms512m -Xmx1024m -Djava.net.preferIPv4Stack=true"